New research shows that inflammation appears to play a role in many chronic diseases and cases of chronic pain.
Not all inflammation is bad
Acute inflammation protects and heals the body after an injury or infection and is essential and normal. For Example, when you have a cut or broken bone, your blood flow to the area is increased which helps repair itself faster. As a result, nerve endings and cells are stimulated at the site of the injury. However, inflammation also recruits the body’s white blood cells, helping to fight off foreign bodies.
The other kind of inflammation, known as systemic inflammation, the buildup of unaddressed inflammation in the body over time. As a result, can have a lasting effect on the body. This consequently causes a wide array of autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. This can cause the body’s immune system to mistakenly issue an inflammatory response.
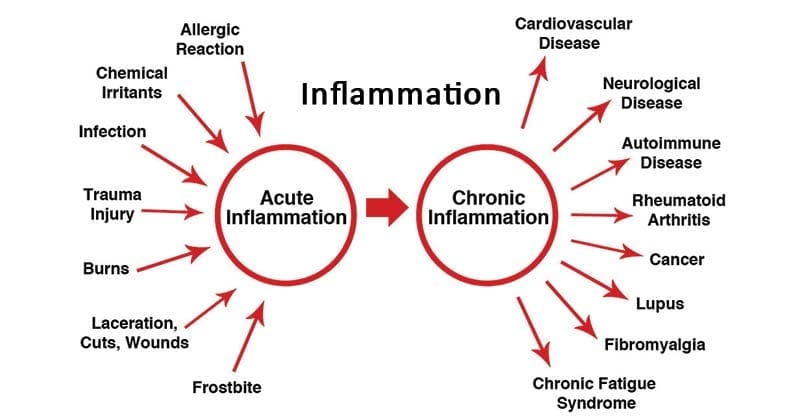
What does this mean for you? What can you do to reduce your risk of chronic inflammation that may play a part in disease?
For Starters, avoid certain things that are proven unhealthy. For instance, are excessive sugar intake, glycotoxins, smoking, and excessive alcohol use.
Anti-inflammatory diet food choices include:
- Generous amounts of fruits and vegetables.
- Healthy fats such as avocados, olive, or coconut oil.
- Small snack portions of nuts ( avoid lectin nuts such as cashews and peanuts.)
- green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collards

These organic, non-GMO plant-based superfoods are a complete source of amino acids and metabolic enzymes. Eating fish on a regular basis, and consuming very little red meat.
Heirloom Barley and Gladiator Barley provide the only stabilized sources of the inflammation-fighting enzyme known as superoxide dismutase. This amazing antioxidant helps lower inflammation throughout your body and reduces your chances of developing chronic disease.